はじめに
こんにちは、最近パンを焼いている者です。
人生で初めて揚げ物しました。こちらバターチキンカレーパンです pic.twitter.com/NygTcteFDD
— nishipy (@iamnishipy) December 4, 2022
これは「Kubernetes Advent Calendar 2022」 6日目の記事です。2020年 と 2021年 も参加させて頂きました。
昨年の「ReplicaSet Controllerは削除するPodをどうやって決めるのか」 に続き、今年もコード読んで勉強した内容を共有させてください。
PLEG is not healthy と NotReadyなノード
KubernetesにおいてノードがNotReadyな状態になる原因はさまざまです。例えばこのように、kubeletのログでPLEG is not healthy: pleg was last seen active 3m20s ago; threshold is 3m0s みたいに出力され、NotReadyになることがあります。PLEG(←?!) が最後にactiveになったのが3分20秒前らしく、閾値の3分を超えているので異常と判断したようです。ちょっと何を言ってるのかわからない、PLEGってそもそも何なんだ…
PLEG とは?
PLEGとは、kubeletの一部で、Pod Lifecycle Event Generatorの略です。概要は、Kubernetesの日本語ドキュメントのコンセプト に載っていました。
一旦desired stateを設定すると、Pod Lifecycle Event Generator(PLEG)を使用したKubernetes コントロールプレーンが機能し、クラスターの現在の状態をdesired state (望ましい状態)に一致させます。そのためにKubernetesはさまざまなタスク(たとえば、コンテナの起動または再起動、特定アプリケーションのレプリカ数のスケーリング等)を自動的に実行します
なるほど、めっちゃ重要そうですね。このドキュメント内にあるPLEGのDesign Proposalへのlinkが埋め込まれているのですが、古いらしくアクセスできません。どうやら古いDesign Proposalは kubernetes/design-proposals-archive に移動されたようです。PLEGのものはこちらです。
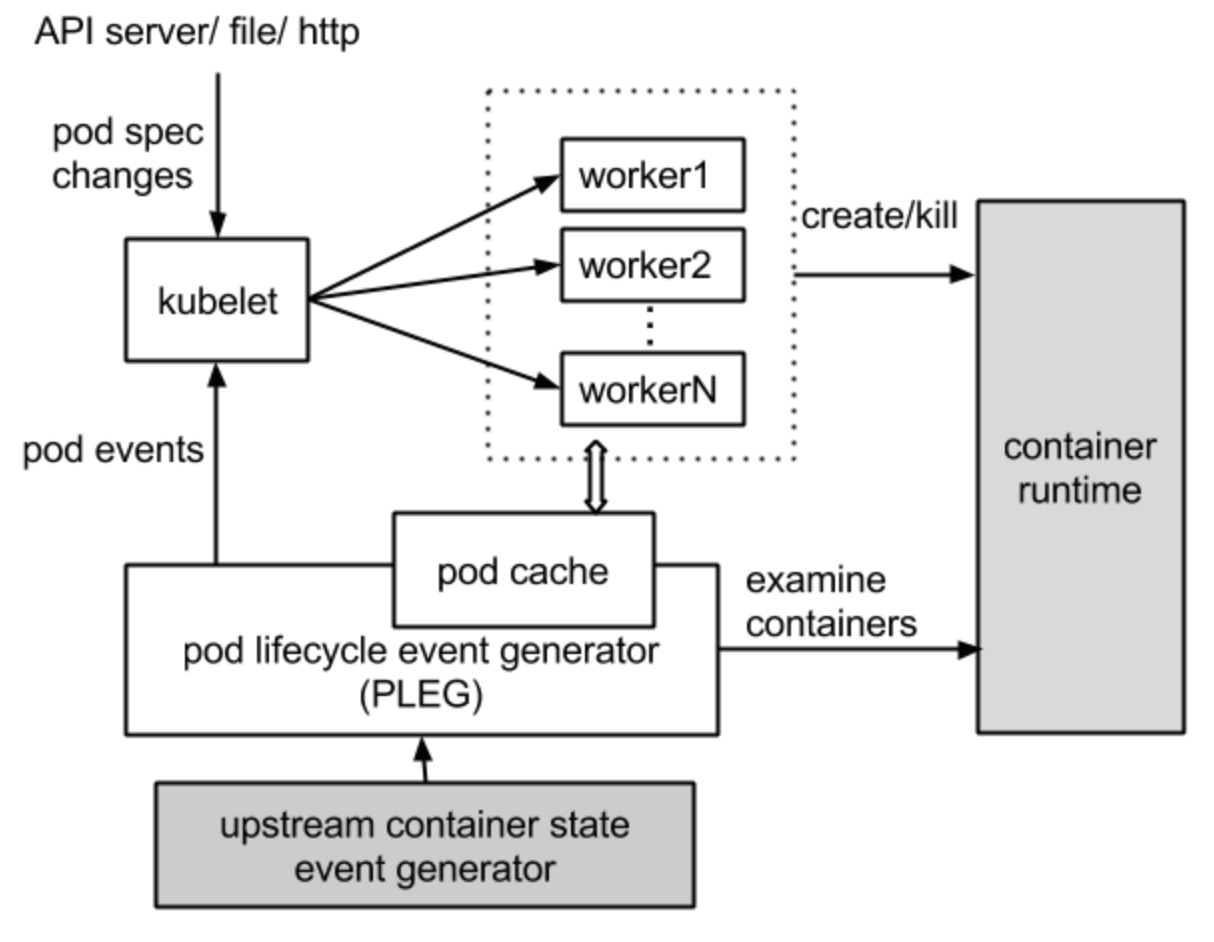
↓の図のように、Container Runtimeおよびkubeletのmain loopとお話するのが仕事のようです。
引用元: https://github.com/kubernetes/design-proposals-archive/blob/main/node/pod-lifecycle-event-generator.md#overview
PLEG の relist 処理
Design Proposalの中の Detect Changes in Container States Via Relisting という章を読むと、relist と呼ばれる処理によってコンテナの状態変化を検知する設計になっています。
- コンテナの状態変化を検知するために、PLEGはすべてのコンテナを定期的にrelistする
- PLEGに任せることですべてのPod Workerが並列でコンテナランタイムをpollingするのを防ぐ
- その後はSyncが必要なPod Workerのみを起動するので、さらに効率がいい
なお、ここでいう Pod Workerは、PLEGと同じくkubeletのコンポーネントの1つです。Pod Workerは個々のPodに対する操作を追跡し、コンテナランタイムなどとの整合性を保証します (雑な訳)。
Runtime Pod Cache とは?
PLEGを調べる上でもう1つ重要そうなのは、Runtime Pod Cacheです。こちらもDesign Proposalがあったので読んでみます。
引用元: https://github.com/kubernetes/design-proposals-archive/blob/main/node/runtime-pod-cache.md#runtime-pod-cache
載っている図はPLEGのとき見たものとほとんど同じですが、PLEGとPod Workerの間に”pod cache”の箱が追記されています。
Runtime Pod Cacheは、すべてのPodの状態を保存するインメモリキャッシュで、Podの同期に使われます。PLEGによって管理され、内部のPodステータスに関するSingle Source of Truth (SSOT) として機能し、kubeletは直接コンテナランタイムに問い合わせる必要はありません。
PLEGはPod Cacheのエントリーを更新する役割を担っており、常にキャッシュを最新の状態に保ちます。以下の順で処理を行い、Podに変化があった場合のみ、対応するPod Lifecycle Eventを生成し、送信する設計のようです。
- Detect change of container state
- Inspect the pod for details
- Update the pod cache with the new PodStatus
その他の情報とソースコード
PLEGのことがふんわりわかったところで、もう少し詳しく調べてみます。
まずこちらの記事が、図が豊富ですごくすごくわかりやすいです。ソースコードの抜粋もあります。
一方、自分でもソースコードを読んでみかったので、以下にまとめてみます。今回読んだソースコードは、Kubernetes 1.25時点のものです。
pkg/kubelet/pleg/pleg.go
PLEGにおける PodLifeCycleEventの種類や関連する構造体、インターフェイスはこちらに定義されています。ContainerStarted、ContainerDied、ContainerRemoved、PodSync、ContainerChanged といった種類のイベントがあります。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
// PodLifeCycleEventType define the event type of pod life cycle events. type PodLifeCycleEventType string const ( // ContainerStarted - event type when the new state of container is running. ContainerStarted PodLifeCycleEventType = "ContainerStarted" // ContainerDied - event type when the new state of container is exited. ContainerDied PodLifeCycleEventType = "ContainerDied" // ContainerRemoved - event type when the old state of container is exited. ContainerRemoved PodLifeCycleEventType = "ContainerRemoved" // PodSync is used to trigger syncing of a pod when the observed change of // the state of the pod cannot be captured by any single event above. PodSync PodLifeCycleEventType = "PodSync" // ContainerChanged - event type when the new state of container is unknown. ContainerChanged PodLifeCycleEventType = "ContainerChanged" ) // PodLifecycleEvent is an event that reflects the change of the pod state. type PodLifecycleEvent struct { // The pod ID. ID types.UID // The type of the event. Type PodLifeCycleEventType // The accompanied data which varies based on the event type. // - ContainerStarted/ContainerStopped: the container name (string). // - All other event types: unused. Data interface{} } // PodLifecycleEventGenerator contains functions for generating pod life cycle events. type PodLifecycleEventGenerator interface { Start() Watch() chan *PodLifecycleEvent Healthy() (bool, error) } |
pkg/kubelet/pleg/generic.go
PLEG関連のソースコードは主にここに書かれています。GenericPLEG構造体はこんな感じです。cache が冒頭説明したRuntime Pod Cacheを指しているのでしょう。kubecontainer.Cache interface のコメントを見ると、キャシュにはコンテナランタイムから見えるすべてのコンテナ/PodのPodStatusが保存されているようです。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
type GenericPLEG struct { // The period for relisting. relistPeriod time.Duration // The container runtime. runtime kubecontainer.Runtime // The channel from which the subscriber listens events. eventChannel chan *PodLifecycleEvent // The internal cache for pod/container information. podRecords podRecords // Time of the last relisting. relistTime atomic.Value // Cache for storing the runtime states required for syncing pods. cache kubecontainer.Cache // For testability. clock clock.Clock // Pods that failed to have their status retrieved during a relist. These pods will be // retried during the next relisting. podsToReinspect map[types.UID]*kubecontainer.Pod } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// Cache stores the PodStatus for the pods. It represents *all* the visible // pods/containers in the container runtime. All cache entries are at least as // new or newer than the global timestamp (set by UpdateTime()), while // individual entries may be slightly newer than the global timestamp. If a pod // has no states known by the runtime, Cache returns an empty PodStatus object // with ID populated. // // Cache provides two methods to retrieve the PodStatus: the non-blocking Get() // and the blocking GetNewerThan() method. The component responsible for // populating the cache is expected to call Delete() to explicitly free the // cache entries. type Cache interface { Get(types.UID) (*PodStatus, error) Set(types.UID, *PodStatus, error, time.Time) // GetNewerThan is a blocking call that only returns the status // when it is newer than the given time. GetNewerThan(types.UID, time.Time) (*PodStatus, error) Delete(types.UID) UpdateTime(time.Time) } |
定数の定義はこんな感じです。relistThreshold は3分ですね。この閾値は PLEG is not healthy: pleg was last seen active XXmYYs ago; threshold is 3m0s というログの中で見ました。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
// plegContainerState has a one-to-one mapping to the // kubecontainer.State except for the non-existent state. This state // is introduced here to complete the state transition scenarios. type plegContainerState string const ( plegContainerRunning plegContainerState = "running" plegContainerExited plegContainerState = "exited" plegContainerUnknown plegContainerState = "unknown" plegContainerNonExistent plegContainerState = "non-existent" // The threshold needs to be greater than the relisting period + the // relisting time, which can vary significantly. Set a conservative // threshold to avoid flipping between healthy and unhealthy. relistThreshold = 3 * time.Minute ) |
*GenericPLEG.Healthy()
GenericPLEG構造体のポインタメソッドとして、Healthy() メソッドがあります。これはPLEG自身がが適切に動作しているかどうか確認するものです。具体的には、2つのrelist間隔が 3分 を超える場合(if elapsed > relistThreshold) に失敗と判断されます。ここ最近親の顔より見た PLEG is not healthy: pleg was last seen active XXmYYs ago; threshold is 3m0s といったエラーを報告しているのがここです。
elapsed は、relistTime というtime.Time型の時刻(たぶん直近のrelistを開始した時刻)から、どれだけの時間が経過したかを測っているように見えます。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
// Healthy check if PLEG work properly. // relistThreshold is the maximum interval between two relist. func (g *GenericPLEG) Healthy() (bool, error) { relistTime := g.getRelistTime() if relistTime.IsZero() { return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg has yet to be successful") } // Expose as metric so you can alert on `time()-pleg_last_seen_seconds > nn` metrics.PLEGLastSeen.Set(float64(relistTime.Unix())) elapsed := g.clock.Since(relistTime) if elapsed > relistThreshold { return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg was last seen active %v ago; threshold is %v", elapsed, relistThreshold) } return true, nil } ~~ func (g *GenericPLEG) getRelistTime() time.Time { val := g.relistTime.Load() if val == nil { return time.Time{} } return val.(time.Time) } |
*GenericPLEG.relist()
PLEGのrelistについては、relist() メソッドで実装されています。relistではコンテナランタイムに問い合わせを行い、Pod/コンテナのリストを取得します。そして、内部のPod/コンテナと比較し、その結果に応じて適宜イベントを生成します。
最初に現在の時刻を取得します。そしてすべてのPod情報をコンテナランタイムから取得したあと、relistTime を直近のrelist()開始時のtimestampに更新します。g.runtime.GetPods(true) で引数にtrueを渡すことで、exitedやdeadなコンテナも含めたリストを取得しています。
取得したリストを用いて、podRecords (Pod/コンテナの情報を持つ内部キャッシュ)のデータを更新しています。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
// relist queries the container runtime for list of pods/containers, compare // with the internal pods/containers, and generates events accordingly. func (g *GenericPLEG) relist() { klog.V(5).InfoS("GenericPLEG: Relisting") if lastRelistTime := g.getRelistTime(); !lastRelistTime.IsZero() { metrics.PLEGRelistInterval.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(lastRelistTime)) } timestamp := g.clock.Now() defer func() { metrics.PLEGRelistDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(timestamp)) }() // Get all the pods. podList, err := g.runtime.GetPods(true) if err != nil { klog.ErrorS(err, "GenericPLEG: Unable to retrieve pods") return } g.updateRelistTime(timestamp) pods := kubecontainer.Pods(podList) // update running pod and container count updateRunningPodAndContainerMetrics(pods) g.podRecords.setCurrent(pods) ~~ |
PodRecordには old と current フィールドがあり、どちらもkubecontainer.Pod 型です。kubecontainer.Pod の構造体はこんな感じで、Pod名、Namespace、コンテナのリストなどの情報が含まれています。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
type podRecord struct { old *kubecontainer.Pod current *kubecontainer.Pod } type podRecords map[types.UID]*podRecord |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
// Pod is a group of containers. type Pod struct { // The ID of the pod, which can be used to retrieve a particular pod // from the pod list returned by GetPods(). ID types.UID // The name and namespace of the pod, which is readable by human. Name string Namespace string // List of containers that belongs to this pod. It may contain only // running containers, or mixed with dead ones (when GetPods(true)). Containers []*Container // List of sandboxes associated with this pod. The sandboxes are converted // to Container temporarily to avoid substantial changes to other // components. This is only populated by kuberuntime. // TODO: use the runtimeApi.PodSandbox type directly. Sandboxes []*Container } |
relistの続きに戻ります。各Podについて、podRecordsの現在(current)と過去(old)の状態を比較し、適宜イベントを生成します。生成されたイベントは、Map eventsByPodID に追加されていきます。そして、このMap eventsByPodID からPodを1つずつ見ていき、もしイベントがある場合には、PodCacheを更新します。
case g.eventChannel <- events[i]: のところで、PodLyifecycleEventのチャネルに空きがあれば、イベントを送信しているのが分かります。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 |
func (g *GenericPLEG) relist() { ~~ // Compare the old and the current pods, and generate events. eventsByPodID := map[types.UID][]*PodLifecycleEvent{} for pid := range g.podRecords { oldPod := g.podRecords.getOld(pid) pod := g.podRecords.getCurrent(pid) // Get all containers in the old and the new pod. allContainers := getContainersFromPods(oldPod, pod) for _, container := range allContainers { events := computeEvents(oldPod, pod, &container.ID) for _, e := range events { updateEvents(eventsByPodID, e) } } } var needsReinspection map[types.UID]*kubecontainer.Pod if g.cacheEnabled() { needsReinspection = make(map[types.UID]*kubecontainer.Pod) } // If there are events associated with a pod, we should update the // podCache. for pid, events := range eventsByPodID { pod := g.podRecords.getCurrent(pid) if g.cacheEnabled() { // updateCache() will inspect the pod and update the cache. If an // error occurs during the inspection, we want PLEG to retry again // in the next relist. To achieve this, we do not update the // associated podRecord of the pod, so that the change will be // detect again in the next relist. // TODO: If many pods changed during the same relist period, // inspecting the pod and getting the PodStatus to update the cache // serially may take a while. We should be aware of this and // parallelize if needed. if err := g.updateCache(pod, pid); err != nil { // Rely on updateCache calling GetPodStatus to log the actual error. klog.V(4).ErrorS(err, "PLEG: Ignoring events for pod", "pod", klog.KRef(pod.Namespace, pod.Name)) // make sure we try to reinspect the pod during the next relisting needsReinspection[pid] = pod continue } else { // this pod was in the list to reinspect and we did so because it had events, so remove it // from the list (we don't want the reinspection code below to inspect it a second time in // this relist execution) delete(g.podsToReinspect, pid) } } // Update the internal storage and send out the events. g.podRecords.update(pid) // Map from containerId to exit code; used as a temporary cache for lookup containerExitCode := make(map[string]int) for i := range events { // Filter out events that are not reliable and no other components use yet. if events[i].Type == ContainerChanged { continue } select { case g.eventChannel <- events[i]: default: metrics.PLEGDiscardEvents.Inc() klog.ErrorS(nil, "Event channel is full, discard this relist() cycle event") } // Log exit code of containers when they finished in a particular event if events[i].Type == ContainerDied { // Fill up containerExitCode map for ContainerDied event when first time appeared if len(containerExitCode) == 0 && pod != nil && g.cache != nil { // Get updated podStatus status, err := g.cache.Get(pod.ID) if err == nil { for _, containerStatus := range status.ContainerStatuses { containerExitCode[containerStatus.ID.ID] = containerStatus.ExitCode } } } if containerID, ok := events[i].Data.(string); ok { if exitCode, ok := containerExitCode[containerID]; ok && pod != nil { klog.V(2).InfoS("Generic (PLEG): container finished", "podID", pod.ID, "containerID", containerID, "exitCode", exitCode) } } } } } if g.cacheEnabled() { // reinspect any pods that failed inspection during the previous relist if len(g.podsToReinspect) > 0 { klog.V(5).InfoS("GenericPLEG: Reinspecting pods that previously failed inspection") for pid, pod := range g.podsToReinspect { if err := g.updateCache(pod, pid); err != nil { // Rely on updateCache calling GetPodStatus to log the actual error. klog.V(5).ErrorS(err, "PLEG: pod failed reinspection", "pod", klog.KRef(pod.Namespace, pod.Name)) needsReinspection[pid] = pod } } } // Update the cache timestamp. This needs to happen *after* // all pods have been properly updated in the cache. g.cache.UpdateTime(timestamp) } // make sure we retain the list of pods that need reinspecting the next time relist is called g.podsToReinspect = needsReinspection } |
Pod Lifecycle Eventの生成は、以下のgenerateEvents() が実施します。最初のif文で分かる通り、状態が前回と状態が変わらない場合は、イベントは生成されません。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
func generateEvents(podID types.UID, cid string, oldState, newState plegContainerState) []*PodLifecycleEvent { if newState == oldState { return nil } klog.V(4).InfoS("GenericPLEG", "podUID", podID, "containerID", cid, "oldState", oldState, "newState", newState) switch newState { case plegContainerRunning: return []*PodLifecycleEvent{{ID: podID, Type: ContainerStarted, Data: cid}} case plegContainerExited: return []*PodLifecycleEvent{{ID: podID, Type: ContainerDied, Data: cid}} case plegContainerUnknown: return []*PodLifecycleEvent{{ID: podID, Type: ContainerChanged, Data: cid}} case plegContainerNonExistent: switch oldState { case plegContainerExited: // We already reported that the container died before. return []*PodLifecycleEvent{{ID: podID, Type: ContainerRemoved, Data: cid}} default: return []*PodLifecycleEvent{{ID: podID, Type: ContainerDied, Data: cid}, {ID: podID, Type: ContainerRemoved, Data: cid}} } default: panic(fmt.Sprintf("unrecognized container state: %v", newState)) } } |
*GenericPLEG.Start()
Start()メソッドでは、goroutineでrelist() メソッドを実行しています。wait.Until() を使用しているので、relistPeriod (= 1秒) 間隔でループします。
|
1 2 3 4 |
// Start spawns a goroutine to relist periodically. func (g *GenericPLEG) Start() { go wait.Until(g.relist, g.relistPeriod, wait.NeverStop) } |
*GenericPLEG.Watch()
Watch() は、PodLifecycleEvent のチャネルを返すメソッドです。kubeletはこのチャネルからイベントを受け取り、 適宜Podの同期処理を行います。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// Watch returns a channel from which the subscriber can receive PodLifecycleEvent // events. // TODO: support multiple subscribers. func (g *GenericPLEG) Watch() chan *PodLifecycleEvent { return g.eventChannel } |
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
さらに、kubelet側でPLEGをどのように呼び出しているか見てみます。いくつかPLEG関連っぽい定数があります。relist間隔は1秒、PodLifecycleEvent用のチャネルのキャパシティは1000のようです。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
const ( ~~snip~~ // Capacity of the channel for receiving pod lifecycle events. This number // is a bit arbitrary and may be adjusted in the future. plegChannelCapacity = 1000 // Generic PLEG relies on relisting for discovering container events. // A longer period means that kubelet will take longer to detect container // changes and to update pod status. On the other hand, a shorter period // will cause more frequent relisting (e.g., container runtime operations), // leading to higher cpu usage. // Note that even though we set the period to 1s, the relisting itself can // take more than 1s to finish if the container runtime responds slowly // and/or when there are many container changes in one cycle. plegRelistPeriod = time.Second * 1 ~~snip~~ ) |
NewMainKubelet() では、必要なすべての内部モジュールとともに新しいKubeletオブジェクトをインスタンス化します。pleg関連の処理はこの辺で、NewGenericPLEG() でGenericPLEGオブジェクトをインスタンス化したあと、kubeletのmain loopのヘルスチェック機構に追加されています。これにより、冒頭で見た PLEG is not healthy: pleg was last seen active XXmYYs ago; threshold is 3m0s といったエラーログが、kubeletのログに表示されていそうです。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// NewMainKubelet instantiates a new Kubelet object along with all the required internal modules. // No initialization of Kubelet and its modules should happen here. func NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *Dependencies, crOptions *config.ContainerRuntimeOptions, hostname string, hostnameOverridden bool, ~~ seccompDefault bool, ) (*Kubelet, error) { ~~ klet.pleg = pleg.NewGenericPLEG(klet.containerRuntime, plegChannelCapacity, plegRelistPeriod, klet.podCache, clock.RealClock{}) klet.runtimeState = newRuntimeState(maxWaitForContainerRuntime) klet.runtimeState.addHealthCheck("PLEG", klet.pleg.Healthy) ~~ } |
kubelet側の Run() メソッドの中で、PLEGも起動(kl.pleg.Start())されているのがわかります。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
// Run starts the kubelet reacting to config updates func (kl *Kubelet) Run(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate) { if kl.logServer == nil { kl.logServer = http.StripPrefix("/logs/", http.FileServer(http.Dir("/var/log/"))) } if kl.kubeClient == nil { klog.InfoS("No API server defined - no node status update will be sent") } // Start the cloud provider sync manager if kl.cloudResourceSyncManager != nil { go kl.cloudResourceSyncManager.Run(wait.NeverStop) } if err := kl.initializeModules(); err != nil { kl.recorder.Eventf(kl.nodeRef, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.KubeletSetupFailed, err.Error()) klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to initialize internal modules") os.Exit(1) } // Start volume manager go kl.volumeManager.Run(kl.sourcesReady, wait.NeverStop) if kl.kubeClient != nil { // Introduce some small jittering to ensure that over time the requests won't start // accumulating at approximately the same time from the set of nodes due to priority and // fairness effect. go wait.JitterUntil(kl.syncNodeStatus, kl.nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, 0.04, true, wait.NeverStop) go kl.fastStatusUpdateOnce() // start syncing lease go kl.nodeLeaseController.Run(wait.NeverStop) } go wait.Until(kl.updateRuntimeUp, 5*time.Second, wait.NeverStop) // Set up iptables util rules if kl.makeIPTablesUtilChains { kl.initNetworkUtil() } // Start component sync loops. kl.statusManager.Start() // Start syncing RuntimeClasses if enabled. if kl.runtimeClassManager != nil { kl.runtimeClassManager.Start(wait.NeverStop) } // Start the pod lifecycle event generator. kl.pleg.Start() kl.syncLoop(updates, kl) } |
Run() メソッドの最後に、syncLoop() メソッドも呼び出しています。syncLoop() の plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch() のところで、PLEGの更新を読み込むためのチャネルを取得し、チャネル経由でPLEGが生成したイベントを受け取っています。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
// syncLoop is the main loop for processing changes. It watches for changes from // three channels (file, apiserver, and http) and creates a union of them. For // any new change seen, will run a sync against desired state and running state. If // no changes are seen to the configuration, will synchronize the last known desired // state every sync-frequency seconds. Never returns. func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) { klog.InfoS("Starting kubelet main sync loop") // The syncTicker wakes up kubelet to checks if there are any pod workers // that need to be sync'd. A one-second period is sufficient because the // sync interval is defaulted to 10s. syncTicker := time.NewTicker(time.Second) defer syncTicker.Stop() housekeepingTicker := time.NewTicker(housekeepingPeriod) defer housekeepingTicker.Stop() plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch() const ( base = 100 * time.Millisecond max = 5 * time.Second factor = 2 ) duration := base // Responsible for checking limits in resolv.conf // The limits do not have anything to do with individual pods // Since this is called in syncLoop, we don't need to call it anywhere else if kl.dnsConfigurer != nil && kl.dnsConfigurer.ResolverConfig != "" { kl.dnsConfigurer.CheckLimitsForResolvConf() } for { if err := kl.runtimeState.runtimeErrors(); err != nil { klog.ErrorS(err, "Skipping pod synchronization") // exponential backoff time.Sleep(duration) duration = time.Duration(math.Min(float64(max), factor*float64(duration))) continue } // reset backoff if we have a success duration = base kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now()) if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) { break } kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now()) } } |
syncLoopIteration() では、さまざまなチャネルを読み込み、与えられたHandlerへディスパッチするメソッドらしいです。そのうちplegCh チャネルは、Runtime Cacheの更新やPodの同期に使用されると説明が載っています。例えば、PLEGのContainerDied (=最新のコンテナの状態がExitedである)というイベントを受け取った場合、kubeletは cleanUpContainersInPod() により、Pod内の当該コンテナインスタンスを削除します。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 |
// syncLoopIteration reads from various channels and dispatches pods to the // given handler. // // Arguments: // 1. configCh: a channel to read config events from // 2. handler: the SyncHandler to dispatch pods to // 3. syncCh: a channel to read periodic sync events from // 4. housekeepingCh: a channel to read housekeeping events from // 5. plegCh: a channel to read PLEG updates from // // Events are also read from the kubelet liveness manager's update channel. // // The workflow is to read from one of the channels, handle that event, and // update the timestamp in the sync loop monitor. // // Here is an appropriate place to note that despite the syntactical // similarity to the switch statement, the case statements in a select are // evaluated in a pseudorandom order if there are multiple channels ready to // read from when the select is evaluated. In other words, case statements // are evaluated in random order, and you can not assume that the case // statements evaluate in order if multiple channels have events. // // With that in mind, in truly no particular order, the different channels // are handled as follows: // // - configCh: dispatch the pods for the config change to the appropriate // handler callback for the event type // - plegCh: update the runtime cache; sync pod // - syncCh: sync all pods waiting for sync // - housekeepingCh: trigger cleanup of pods // - health manager: sync pods that have failed or in which one or more // containers have failed health checks func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler, syncCh <-chan time.Time, housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time, plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent) bool { ~~ case e := <-plegCh: if e.Type == pleg.ContainerStarted { // record the most recent time we observed a container start for this pod. // this lets us selectively invalidate the runtimeCache when processing a delete for this pod // to make sure we don't miss handling graceful termination for containers we reported as having started. kl.lastContainerStartedTime.Add(e.ID, time.Now()) } if isSyncPodWorthy(e) { // PLEG event for a pod; sync it. if pod, ok := kl.podManager.GetPodByUID(e.ID); ok { klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop (PLEG): event for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "event", e) handler.HandlePodSyncs([]*v1.Pod{pod}) } else { // If the pod no longer exists, ignore the event. klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (PLEG): pod does not exist, ignore irrelevant event", "event", e) } } if e.Type == pleg.ContainerDied { if containerID, ok := e.Data.(string); ok { kl.cleanUpContainersInPod(e.ID, containerID) } } ~~ |
pkg/kubelet/runtime.go
klet.runtimeState.addHealthCheck("PLEG", klet.pleg.Healthy) でPLEGのヘルスチェックがkubelet runtimeのヘルスチェックに追加されていた箇所もついでに見てみます。addHealthCheck() で追加された各ヘルスチャック用の関数が、for文で呼び出され、評価されています。エラー発生時には、fmt.Errorf("%s is not healthy: %v", hc.name, err) という出力形式で表示されるらしく、PLEG is not healthy: pleg was last seen active XXmYYs ago; threshold is 3m0s というエラーメッセージはここから来てたんですね〜。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
// A health check function should be efficient and not rely on external // components (e.g., container runtime). type healthCheckFnType func() (bool, error) type healthCheck struct { name string fn healthCheckFnType } func (s *runtimeState) addHealthCheck(name string, f healthCheckFnType) { s.Lock() defer s.Unlock() s.healthChecks = append(s.healthChecks, &healthCheck{name: name, fn: f}) } func (s *runtimeState) runtimeErrors() error { s.RLock() defer s.RUnlock() errs := []error{} if s.lastBaseRuntimeSync.IsZero() { errs = append(errs, errors.New("container runtime status check may not have completed yet")) } else if !s.lastBaseRuntimeSync.Add(s.baseRuntimeSyncThreshold).After(time.Now()) { errs = append(errs, errors.New("container runtime is down")) } for _, hc := range s.healthChecks { if ok, err := hc.fn(); !ok { errs = append(errs, fmt.Errorf("%s is not healthy: %v", hc.name, err)) } } if s.runtimeError != nil { errs = append(errs, s.runtimeError) } return utilerrors.NewAggregate(errs) } |
今後のPLEG
KEPの中に、Kubelet Evented PLEG for Better Performance というのを見つけました。気が向いたら読んでみたいと思います。
さいごに
数多あるkubeletのコンポーネントの1つであるPLEGについて調べてみました。Advent Calendar期間しかブログ更新する気が起きないので、今年も開催もいただき感謝です。
Kubernetesな皆さま、2022年ありがとうございました。よいお年を〜
References
- “PLEG is not healthy” errors on OpenShift nodes. – Red Hat Customer Portal
- コンセプト – Kubernetesドキュメント
- Pod Lifecycle Event Generator: Understanding the “PLEG is not healthy” issue in Kubernetes – Red Hat Developer
- kubernetes/design-proposals-archive – GitHub
- kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/pleg at release-1.25 – GitHub
- Isuue: Kubelet Evented PLEG for Better Performance – GitHub
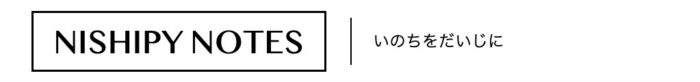


コメント